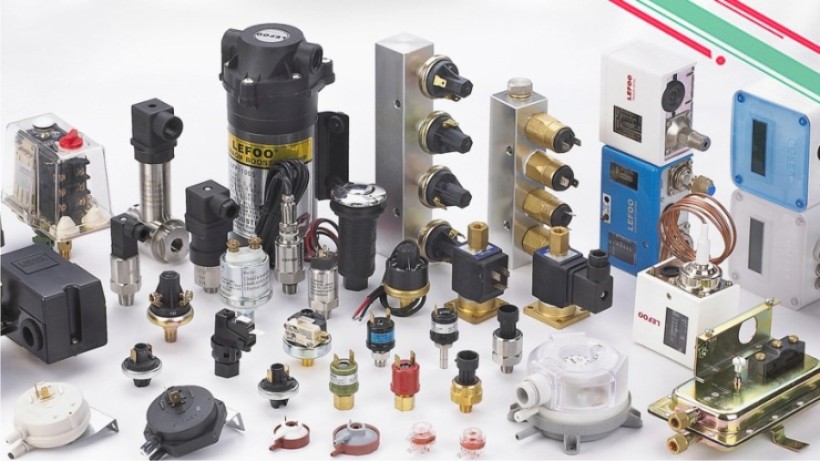
Pressure sensors are essential components in a wide range of industrial systems. Whether in HVAC, pneumatic automation, hydraulic systems, or air compressors, the right pressure sensor ensures efficiency, safety, and reliability.
But with so many models and technologies available, how do you choose the right pressure sensor for your specific application? In this article, we’ll guide you through the key factors to consider.
What Is a Pressure Sensor?
A pressure sensor is a device that measures the pressure of gases or liquids. It converts physical pressure into an electrical signal that can be read and processed by a control system or monitoring device.
Pressure sensors are used in:
-
Industrial automation
-
HVAC systems
-
Hydraulic and pneumatic equipment
-
Air compressors
-
Water treatment systems
-
Medical devices
-
And much more
Types of Pressure Sensors
Before choosing a pressure sensor, it’s important to understand the main types:
1. Absolute Pressure Sensors
Measure pressure relative to a perfect vacuum (0 bar). Common in aerospace and high-precision applications.
2. Gauge Pressure Sensors
Measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. These are the most commonly used in industrial applications.
3. Differential Pressure Sensors
Measure the difference between two pressure points. Ideal for monitoring filters, flow rates, or pressure drops across systems.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Pressure Sensor
1. Application Type
Understand where the sensor will be used: HVAC, water systems, oil circuits, pneumatic tools, etc. Each application may require a different sensor specification.
2. Pressure Range
Define the minimum and maximum pressures your system will experience. Choose a sensor with a range slightly above your operating pressure to ensure accuracy and durability.
3. Medium Compatibility
What fluid or gas will the sensor measure? Make sure the sensor materials are compatible with the medium (e.g., water, oil, refrigerant, air, corrosive liquids).
4. Environmental Conditions
Consider temperature range, humidity, vibration, and exposure to chemicals or dust. Some industrial environments require rugged or sealed sensors.
5. Output Signal Type
Sensors may offer analog (e.g., 0-10V, 4-20mA) or digital outputs (e.g., I²C, SPI, RS485). Choose one that’s compatible with your control system or PLC.
6. Accuracy and Stability
Depending on your process, you may need a high-accuracy sensor with low drift over time. This is especially true in critical operations like medical devices or precision automation.
Common Industrial Applications and Sensor Recommendations
HVAC Systems
Use pressure sensors for refrigerant monitoring, air flow, and differential pressure across filters.
Recommended: Compact, accurate sensors with good temperature tolerance.
Pneumatic Systems
Measure and control compressed air in automation lines.
Recommended: Robust sensors with fast response times.
Hydraulic Systems
Monitor fluid pressure to protect pumps and actuators.
Recommended: High-pressure sensors with reinforced construction.
Water Treatment
Used for monitoring pressure in filtration systems and pipelines.
Recommended: Corrosion-resistant sensors, often in stainless steel.
Why Choosing the Right Pressure Sensor Matters
Using the wrong sensor can result in:
-
System failures
-
Inaccurate readings
-
Safety risks
-
Increased maintenance costs
Choosing the right sensor, on the other hand, brings:
-
Operational efficiency
-
System protection
-
Long-term reliability
-
Cost savings
Selecting the ideal pressure sensor for your industrial application is a crucial step in ensuring performance and safety. By understanding the requirements of your system and the characteristics of different sensors, you can make a confident and informed choice.
At Lefoo, we offer a complete range of pressure sensors for various industrial applications, backed by quality, precision, and support.
Need help finding the right pressure sensor?
Talk to our specialists and let’s find the perfect solution for your system.
Lefoo | Smart Control. Reliable Performance.